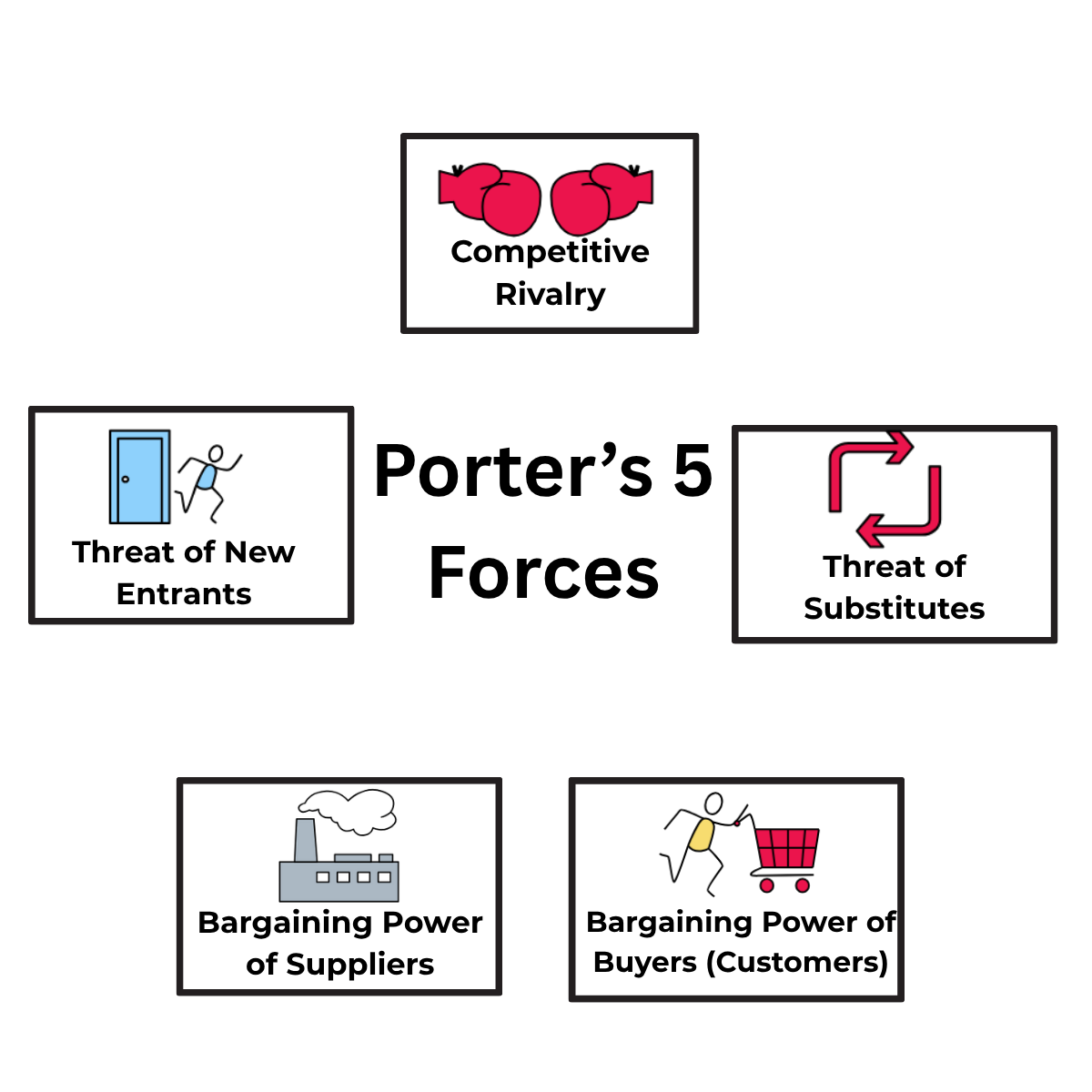
Porter's 5 Forces is a framework invented by Harvard professor Michael Porter in 1979. It identifies and analyzes competition in a market.
He writes "The essence of strategy formulation is coping with competition. Yet it is easy to view competition too narrowly and too pessimistically"
Rather than only looking at other companies in the same market, the tool looks at broader competition for a company's products or services:
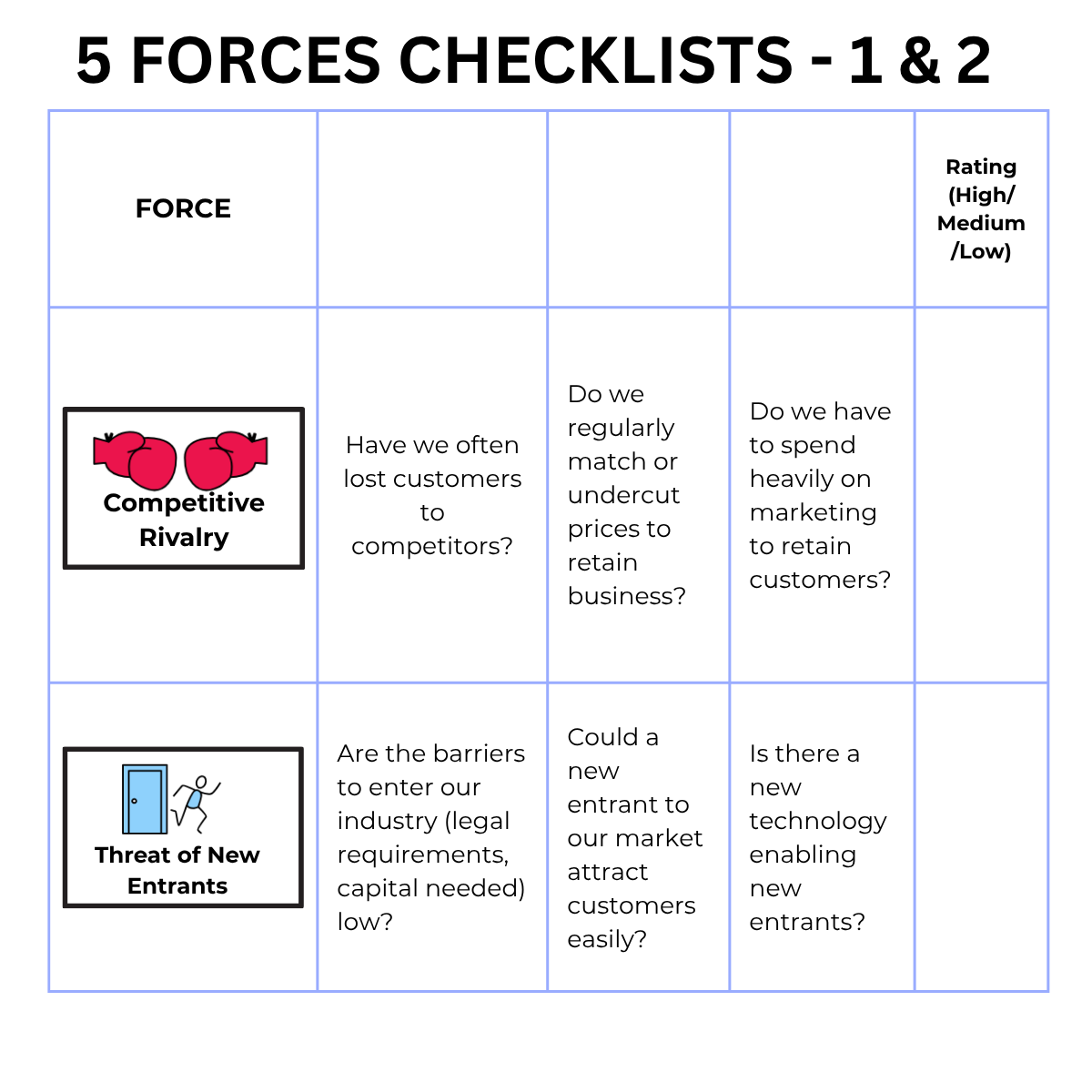
🤝 Competitive Rivalry
🚪 Threat of New Entrants
🏭 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
🛍️ Bargaining Power of Buyers
🔄 Threat of Substitutes
(Source - Harvard Business Review, March 1979)
Definition - level of competition between existing firms
Impact : High competition can mean price wars, leading to lower margins. Competitors can have strong marketing campaigns, making customer aquisition hard.
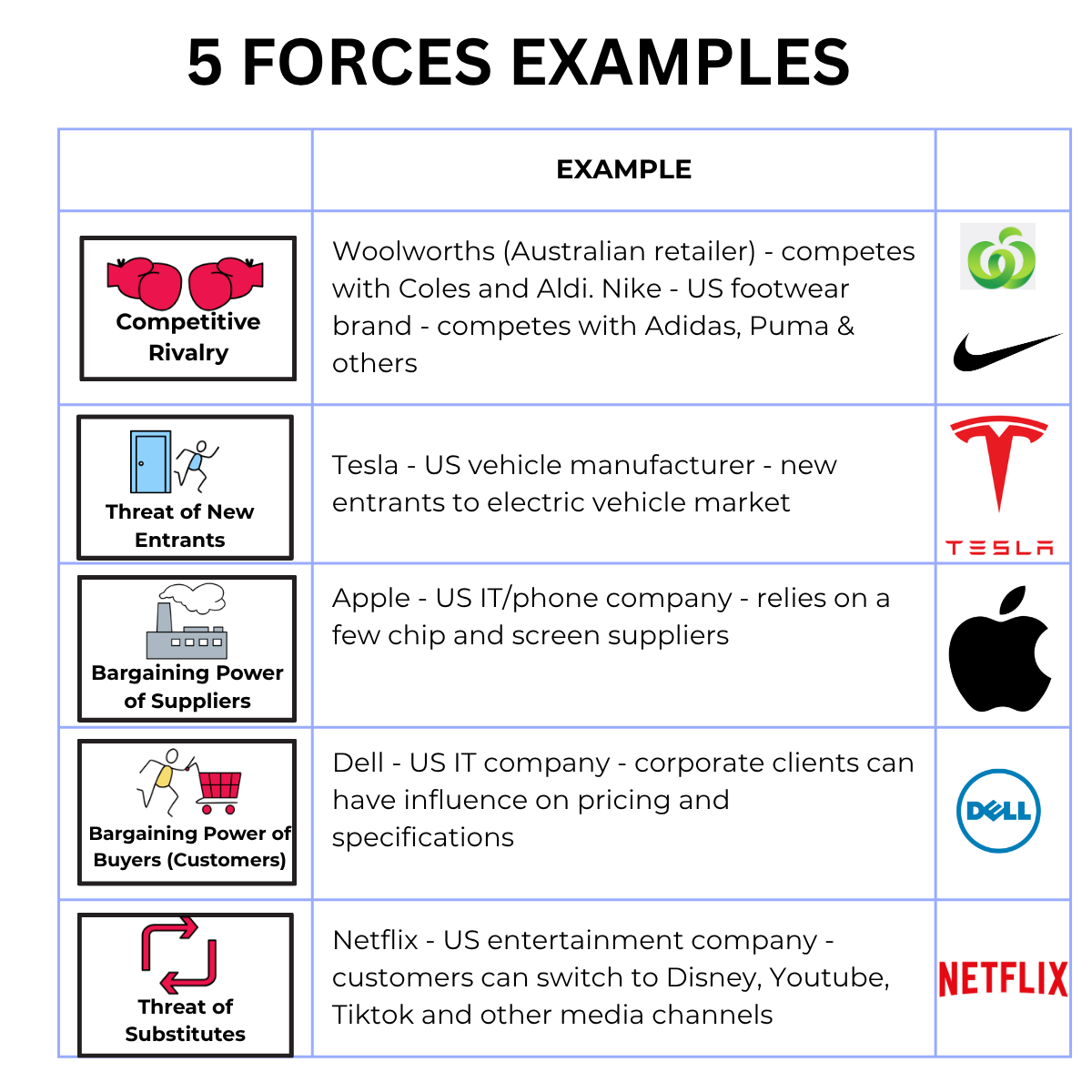
Examples: Coles & Woolworths - retailers in Australia. Nike - competes with Adidas, Puma & others.
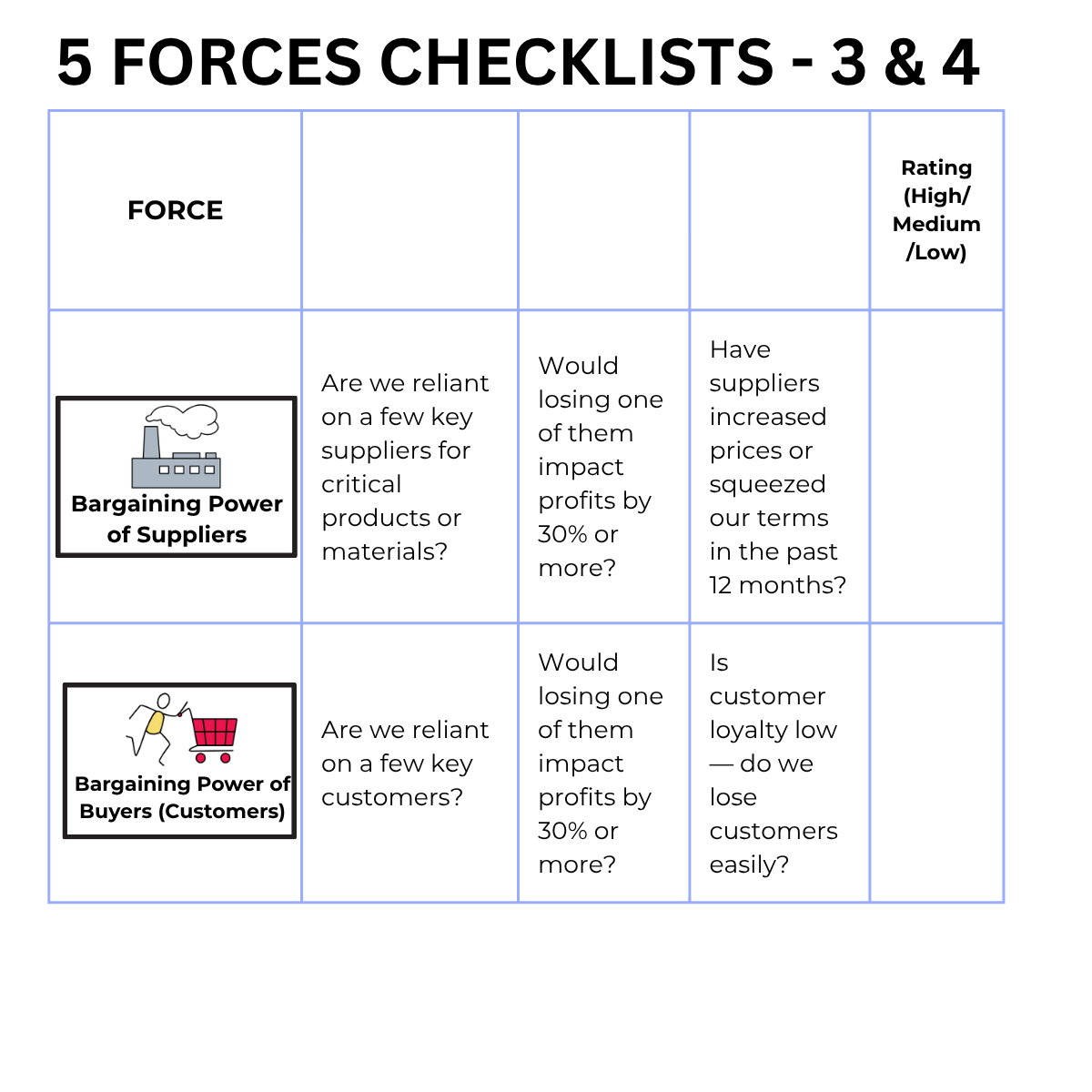
Definition: risk of new companies entering the market, increasing the competition.
Impact : new entrants may lower prices or offer new products that compete with the existing offering.
Example : Tesla lead the way in developing electric vehicles, but other companies have entered the electric vehicle market.
Definition: ability of suppliers to control prices or volumes of production.
Impact : where a company is reliant on a few suppliers, the company may have to pay high prices and/or face restrictions in supply.
Example: Apple is reliant on a few chip manufacturers
Definition; the ability of buyers (customers) to demand lower prices, new or improved products and better services.
Impact : where a company is reliant on a few customers, there is a higher risk of the customer dictating lower prices or different product/service features.
Example : Dell - corporate buyers can demand lower prices and high quality service & products.
Definition; the risk that customers will switch to another product or service that satifies the same need.
Impact : substitutes not only come from competitiros in the same industry, but products or services which satisfy a need.
Example : Netflix competes with other entertainment services - Disney, Spotify, Youtube.

| 🔍 Force | 📊 Level | 🏢 Examples | 📝 Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🤝 Competitive Rivalry | High |
|
Both face intense rivalry: Woolworths competes closely with Coles and Aldi; Nike competes globally with Adidas, Puma, and others. |
| 🚪 Threat of New Entrants | Moderate |
|
Tesla disrupted the electric vehicle industry, but new startups continue to emerge. |
| 🏭 Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Moderate |
|
Apple relies on a few key chip and screen suppliers; few alternatives exist. |
| 🛍️ Bargaining Power of Buyers | High |
|
Dell's corporate clients have negotiating power on price/specs. |
| 🔄 Threat of Substitutes | High |
|
Netflix competes with YouTube, TikTok, and Disney+. |
| 🔍 Force | ⚙️ Level | 📝 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🤝 Competitive Rivalry | High | Nike competes with major global brands like Adidas, Puma, and Under Armour. Competition is intense. |
| 🚪 Threat of New Entrants | Low | Nike and its competititors like Addidas have strong brands with loyal followings. They also have established supply chain controls. These create entry barriers. |
| 🏭 Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Low | Nike sources from many global suppliers, giving it leverage in pricing and flexibility to switch vendors if needed. |
| 🛍️ Bargaining Power of Buyers | Moderate | Customers can easily switch brands based on price, design, or trend. However, individual buyer influence is limited. |
| 🔄 Threat of Substitutes | Moderate | Alternatives include other athletic and fashion wear brands. Nike mitigates this with strong innovation and performance branding. |
Actions : Nike should focus on the competitive rivalry with Addidas and others:
| 🔍 Force | ⚙️ Level | 📝 Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🤝 Competitive Rivalry | High | Intense competition from Coles, plus Aldi, Costco, and IGA. Price wars, promotions, and customer loyalty programs fuel rivalry. |
| 🚪 Threat of New Entrants | Low | High capital requirements, strong brand loyalty, established supply chains, and regulatory barriers make it hard for new entrants to scale in Australia. |
| 🏭 Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Low | Major supermarkets dominate supplier negotiations. |
| 🛍️ Bargaining Power of Buyers | Moderate | Customers are price sensitive and have options like Aldi and online delivery. However, Woolworths and Coles maintain strong loyalty and reach. |
| 🔄 Threat of Substitutes | Moderate | Substitutes include local markets, direct-from-farm produce, meal delivery services, and specialty food retailers. These are growing but still secondary to mainstream shopping. |
Actions : Woolworths should focus on the competitive rivalry with Coles and others: