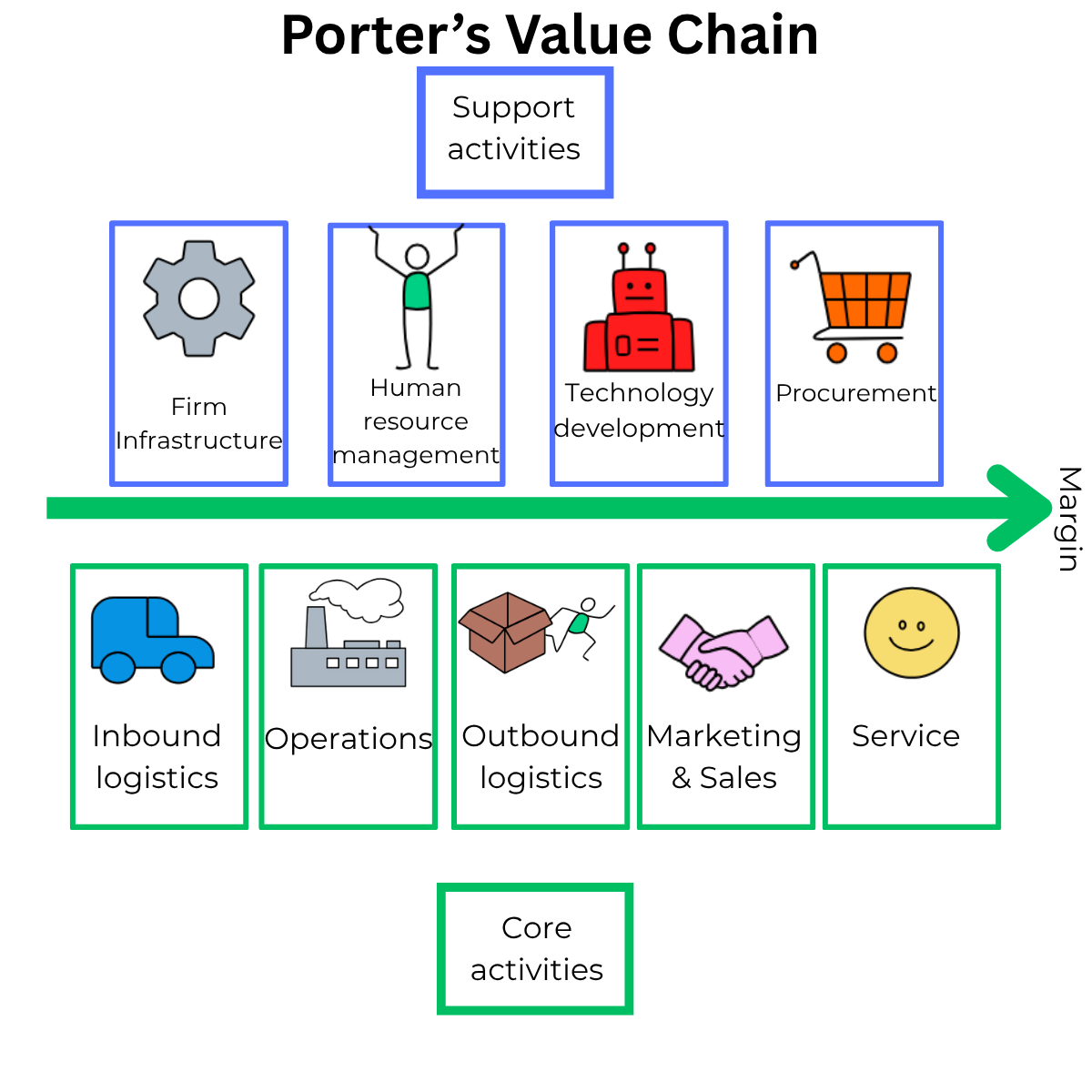
Porter's Value Chain is a framework invented by Harvard professor Michael Porter. It identifies how a company creates value and where it can improve.
It follows on from Porter's 5 Forces tool, which looks at the external competitive environment.
Porter's value chain looks at the internal factors in a business by looking at Core Activities and Support Activities.

Core Activities are the 5 direct value-generating activities — the creation, sale, and delivery of a product or service.
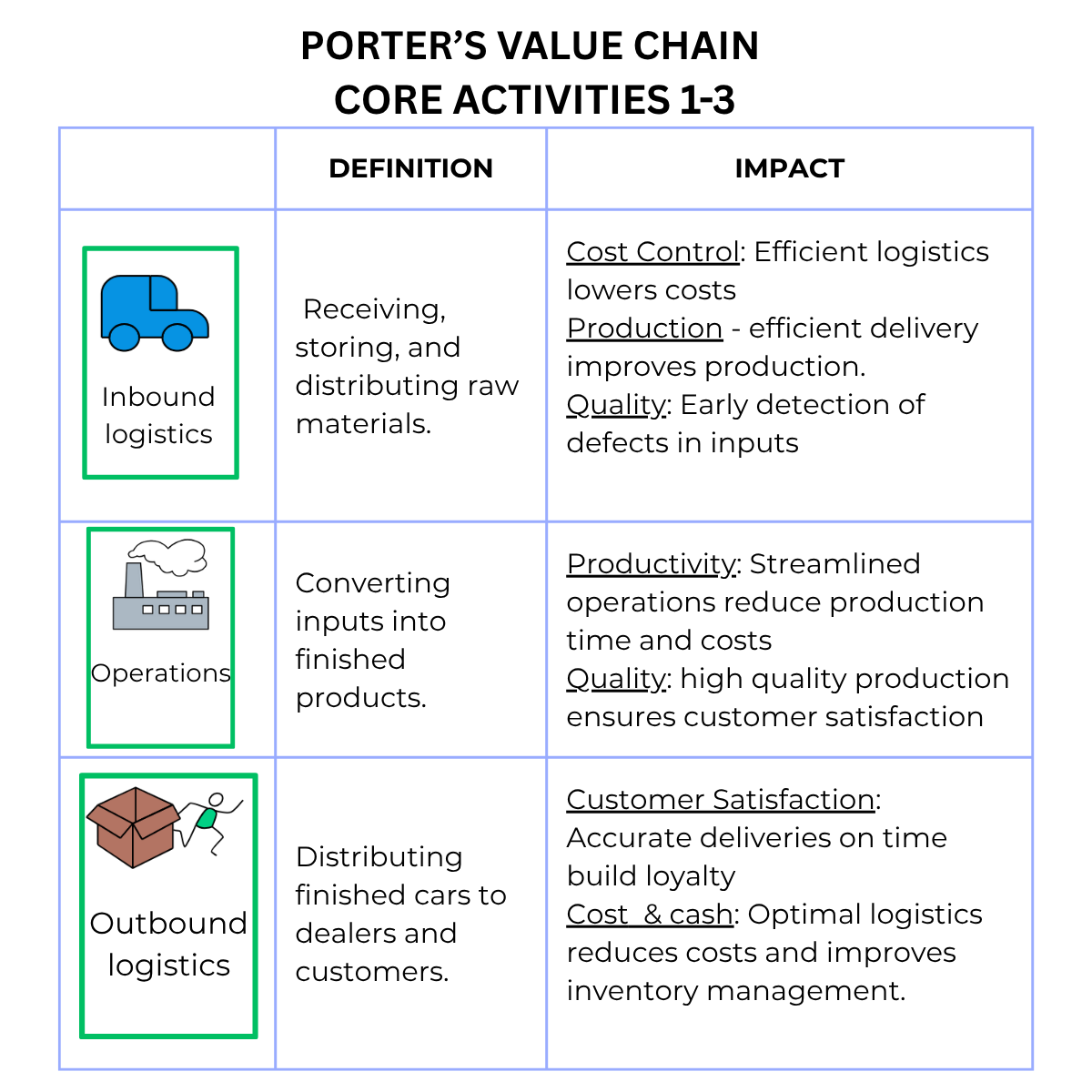
📥 Inbound logistics – receiving and storing raw materials.
🏭 Operations – converting inputs into finished products.
🚚 Outbound logistics – distributing products to customers.
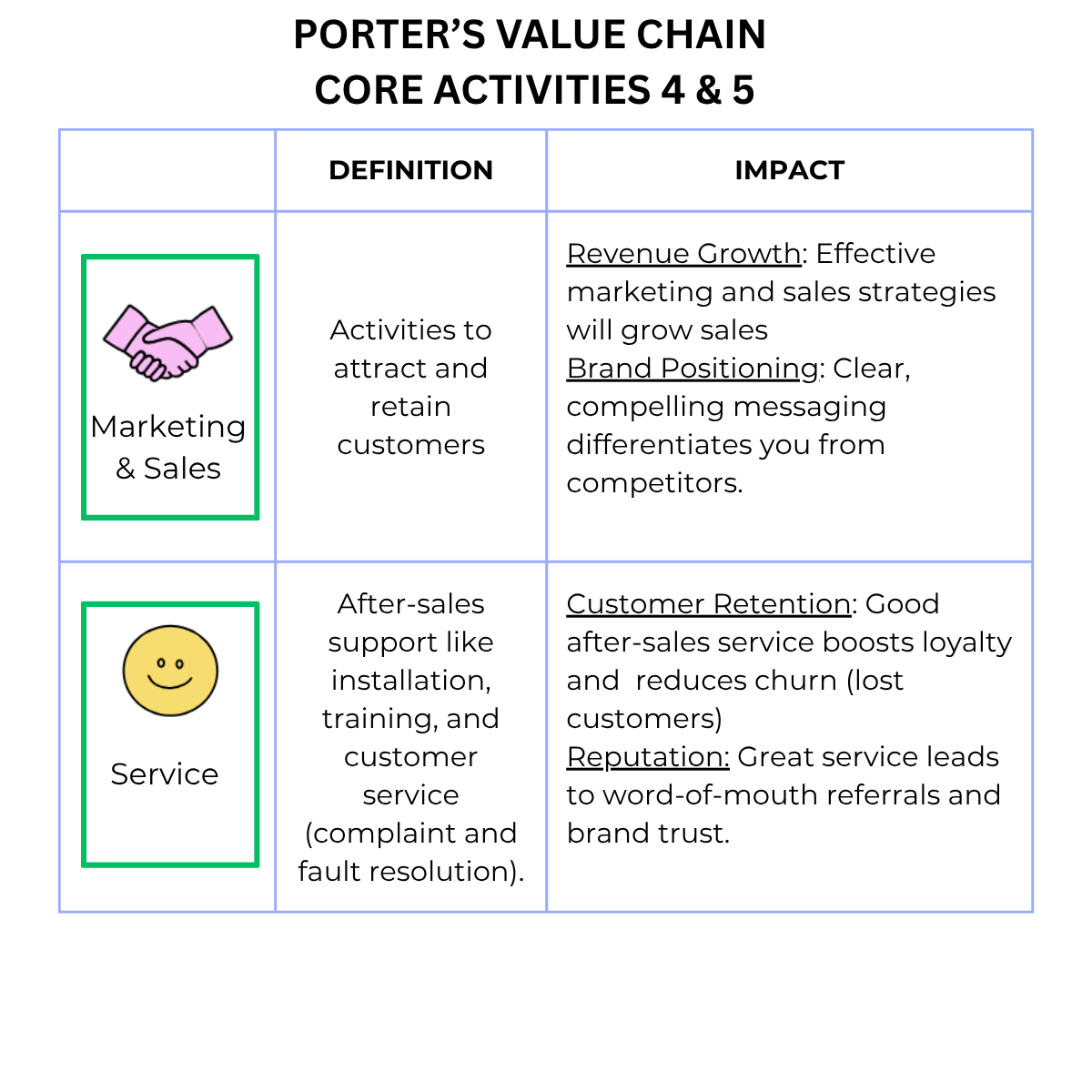
📢 Marketing & sales – persuading customers to buy.
🛠️ Service – after-sales support and maintenance.
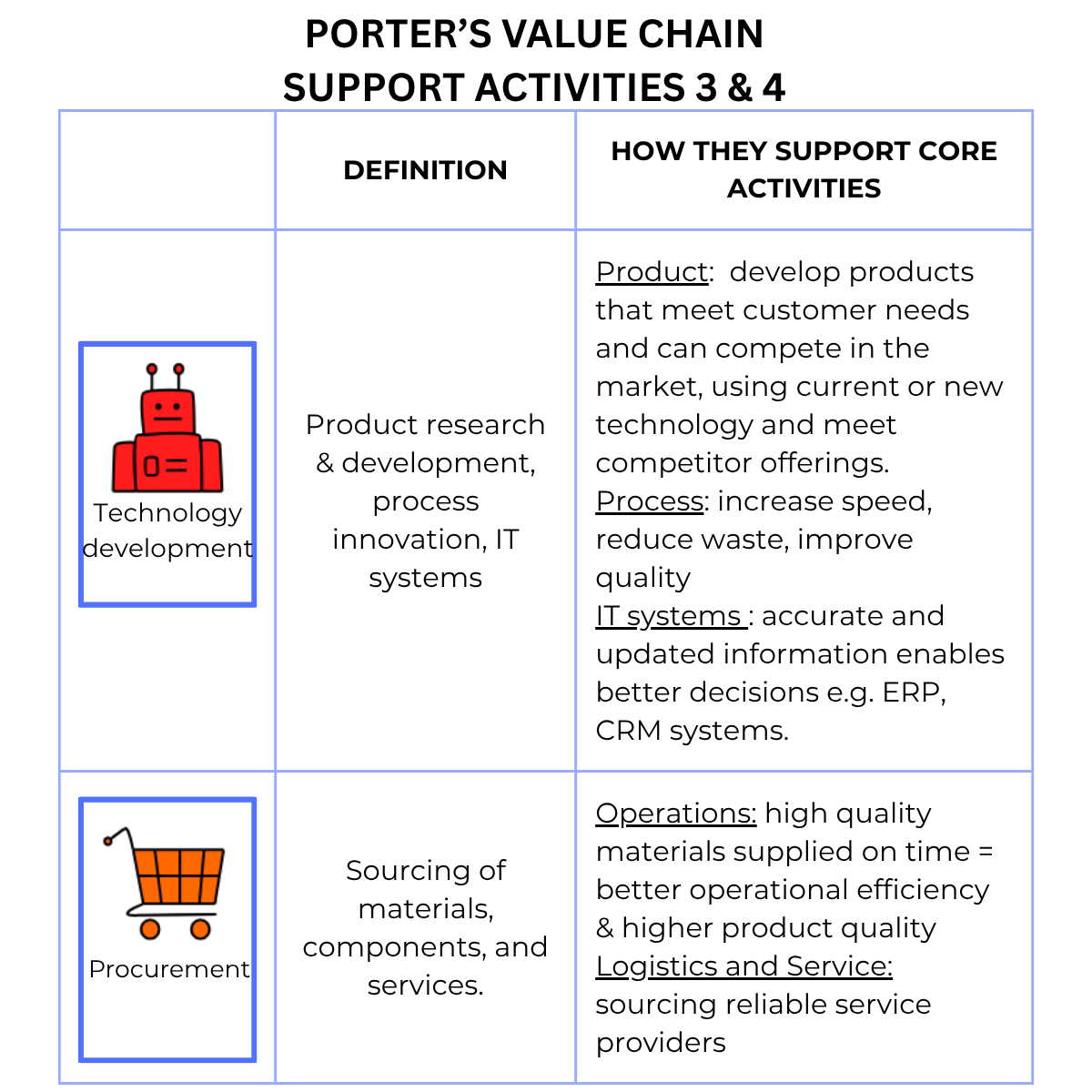
Support Activities are the 4 activities that are needed to support the core activities.
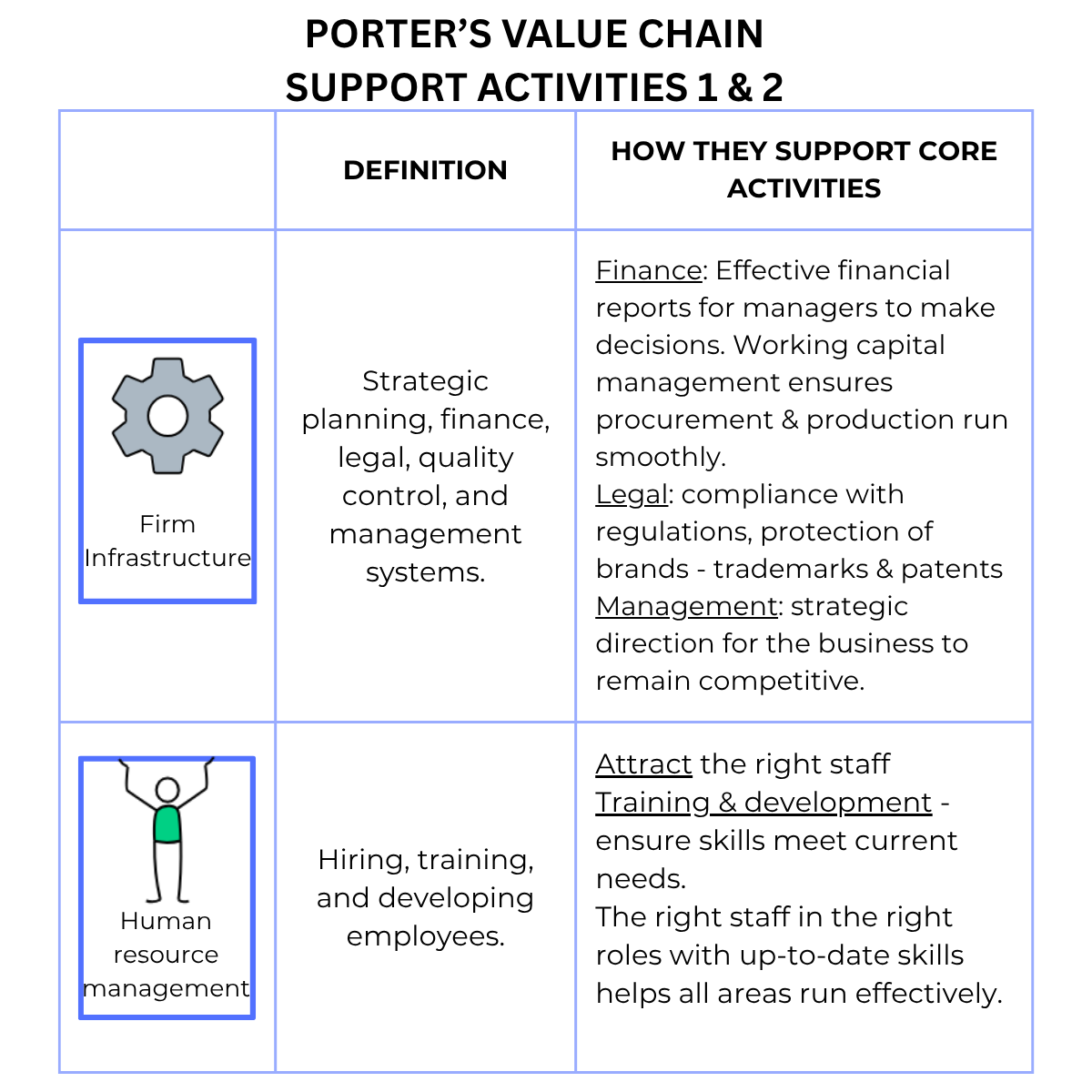
⚙️ Firm Infrastructure – Strategic planning, finance, legal, quality control, and management systems that guide and support the business.
🧑💼 Human Resource Management – Hiring, training, and developing employees to ensure the right people are in the right roles with the right skills.
🤖 Technology Development – Product research and development, process innovation, and IT systems that improve efficiency and competitiveness.
🛒 Procurement – Sourcing of materials, components, and services needed to support operations and deliver value to customers.
| 🏃Activity | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| 📥 Inbound logistics | Just-In-Time (JIT) system:Toyota minimised inventory costs by having parts delivered exactly when needed in the production process. Close supplier relationships:a network of reliable suppliers with joint quality improvement programs. |
| 🏭 Operations | Toyota Production System (TPS): A globally recognized lean manufacturing approach emphasizing Kaizen(continuous improvement) and Jidoka(automation with human intelligence). |
| 🚚 Outbound logistics | Global logistics network:coordinates shipping from factories to dealers efficiently. Regional production:Builds vehicles closer to the markets they serve (e.g., North America, Europe), reducing shipping costs and time. |
| 📢 Marketing & sales | Strong brand image:Known for reliability, quality, fuel efficiency, and innovation. |
| 🛠️ Service | Extensive service network: Authorised service centers globally with trained technicians and standardized service procedures. |
Getting materials, supplies, or products into your business.
The way we create or deliver our product/service.
Getting products/services to the customer.
How we attract and convert customers.
How we support customers after a sale.
Leadership, finance, admin, and planning.
Hiring, training, managing your team.
Using tools to improve operations or customer experience.
How we source products, services, or materials.