Being humans, we often fool ourselves, both in business and in our personal lives. If we are aware of thinking traps, we are less likely to fall into them.
One thinking trap is the "Survivorship Bias".
Survivorship bias is a logical error that happens when we focus only on the people or things that “survived” a process and ignore those that did not. This leads to overly optimistic or misleading conclusions.
It’s a type of selection bias — we see the winners, but not the many failures that dropped out along the way. 🏁
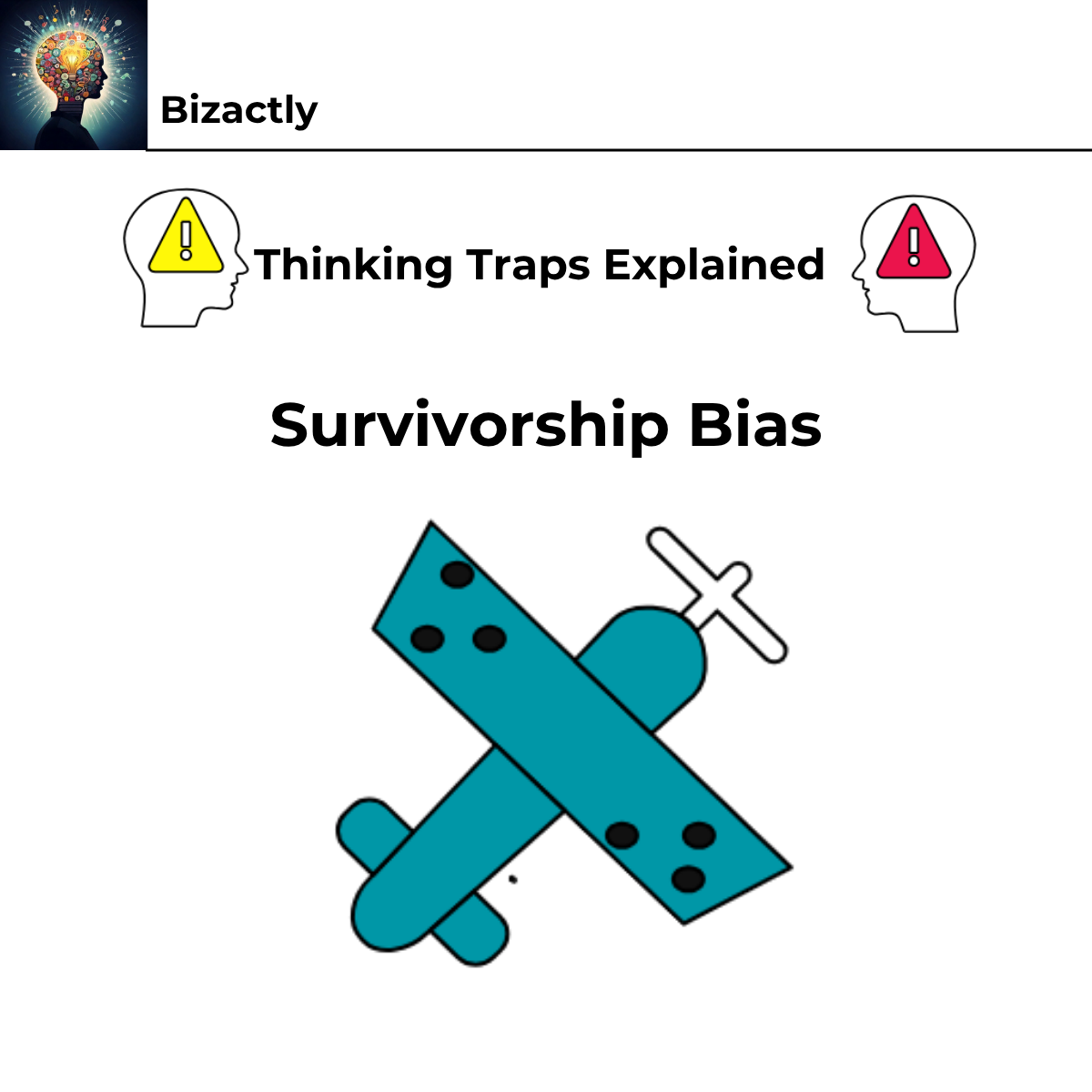
During World War II, the U.S. Army Air Force wanted to reinforce aircraft that returned from missions full of bullet holes. They noticed most hits were on the wings and fuselage, but fewer on the engines. 🛩️
At first, engineers suggested adding armor where the bullet holes were most common. But statistician Abraham Wald realized this was a classic case of survivorship bias — they were only looking at planes that came back safely! 🚫
Wald concluded that planes hit in the engines didn’t return at all. Therefore, the armor should be added where there were no bullet holes, because that’s where damage was fatal. 🎯
Lesson: Don’t just study survivors — study what’s missing.


📈 Investment Funds: Reports showing the “average 10-year return” of mutual funds often exclude those that closed or failed. This makes the industry appear far more profitable than it really is.
🏢 Startup Success Stories: Reading about Airbnb, Tesla, or Apple can make entrepreneurship seem easy. But most startups — even those with smart founders — fail. We rarely hear those stories, leading to an inflated belief in success odds.
🧑💼 Career Advice: Interviews with CEOs or “self-made” millionaires emphasize certain habits (like waking up early or meditating), but ignore thousands of others with the same habits who didn’t succeed. The failures are invisible.
💰 Venture Capital: VC firms proudly showcase their unicorns (like Uber or Stripe) while ignoring the many portfolio companies that didn’t survive. This distorts the perceived success rate of venture investing.
📚 Product Testimonials: Companies display glowing reviews but rarely include dissatisfied customers. This makes products seem more reliable than they may actually be.



❓ Questions to Ask Yourself:
🤔 What information might be missing from this success story?
🕵️ Who or what didn’t make it, and why?
⚖️ Am I judging the winners or the process fairly?
📊 Would the same conclusion hold if I included failures?


🌐 Resources:
🌐 BBC Future – The Hidden Perils of Survivorship Bias
📘 Harvard Business Review – Beware of Survivorship Bias
🧩 Farnam Street – Learn from Failures, Not Just Successes